Integrating Autometrics in your Github CI/CD
Autometrics can be integrated into your Github CI/CD pipeline to automatically review how well is your new feature instrumented.
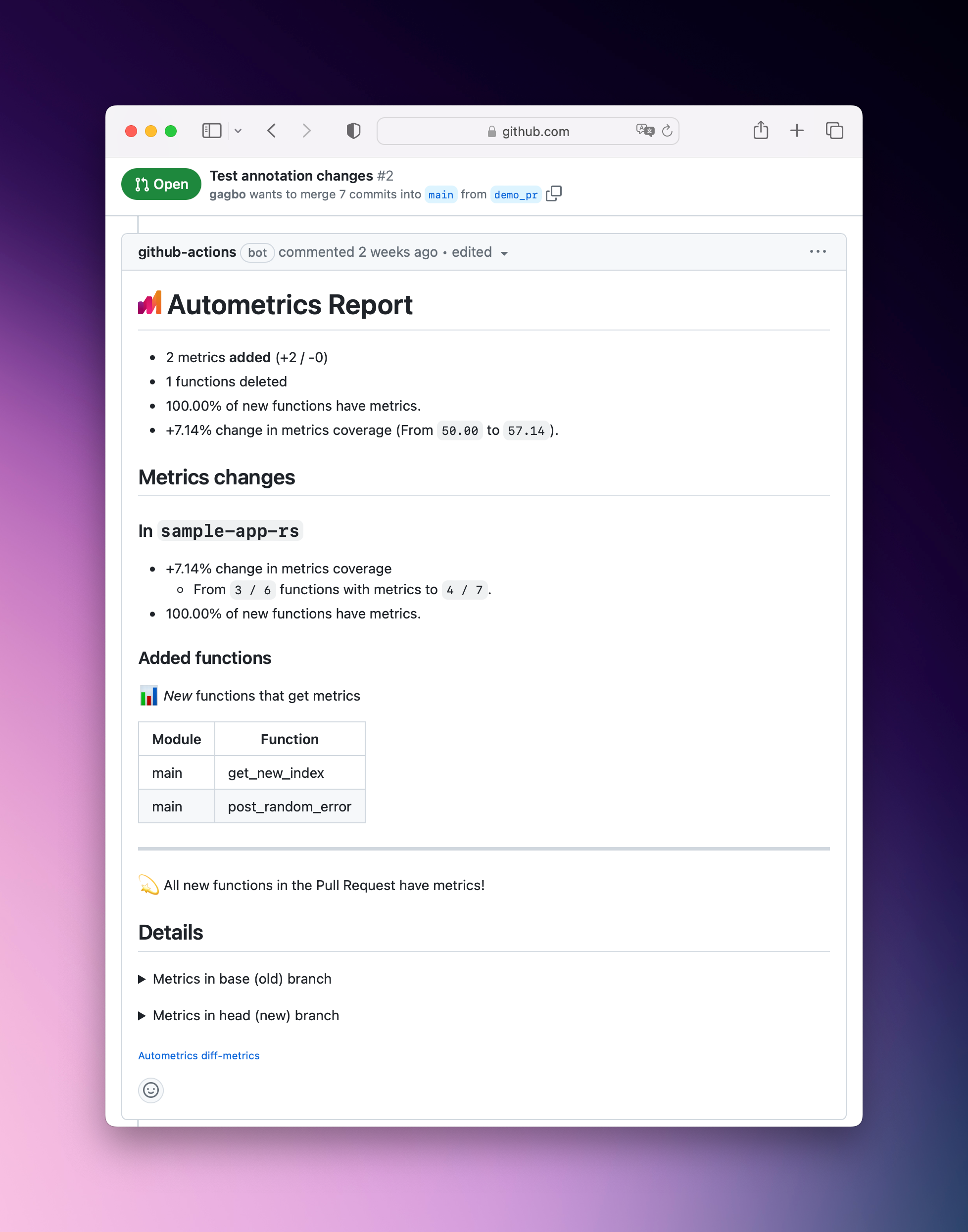
Github Action diff-metrics (opens in a new tab) creates an Autometrics report that will show you a useful summary of the metrics that will be reported without needing to go through the diff manually.
Usage
Note: the action currently only works on Rust projects. Support for other languages is coming soon. See the Language support section for more details.
On each Pull Request diff-metrics does the following:
- traverses the diff looking for changes in the Autometrics instrumentation;
- writes comments on a pull request showing you the monitoring impact of the incoming pull request;
- saves the data used to compute this report as workflow artifacts. Workflow artifacts stay private to the repository that created them, but this allows for further processing if need be.
The job must only contain the checkout step and the diff-metrics step, the steps that follow within the job would act on an older version of the repository.
name: Metrics report
on: [pull_request]
jobs:
build:
# The task only runs on linux x64 machines.
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# Permissions are necessary to be able to edit and write comments on the PR
permissions:
issues: write
pull-requests: write
repository-projects: read
contents: read
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: autometrics-dev/diff-metrics@v1
with:
gh-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
rust-roots: |
.Configuration
-
gh-token: a github token that gives access to- the PR
- the repo
- read/write access to comments on issues/PR
The built-in
${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}will work, you do not need to create a new one. To make the built-in token work, the job must be given a specific set of permissions. The permissions added in the "Example Usage" section show the minimal set of permissions needed. -
rust-roots: a list of project roots for rust projects, one root per line. The values are given relative to the root of the repository, and should point to the directory containing theCargo.tomldirectory. -
retention-days: the number of days to keep the list of functions as workflow artifacts (opens in a new tab). By default it will use the same retention settings as the settings in the repository (by settingretention-daysto 0) -
am-version: a string that allows to choose the version ofam_listto download/use. You can skip the patch (e.g.0.2) or the minor (e.g.0) to tell the action to download the latest version that falls within the bound. Defaults to an empty string (""), which means "download the latest version, semver-wise"
| Argument | Mandatory |
|---|---|
| gh-token | yes |
| rust-roots | no |
| retention-days | no |
| am-version | no |
Monorepo example for rust-roots
In the case of a mono repo that would look like
.
├── project-a
│ ├── README.md
│ │ ...
│ └── Cargo.toml
├── project-b
│ ├── README.md
│ │ ...
│ └── Cargo.toml
├── project-c
│ ├── README.md
│ │ ...
│ └── Cargo.toml
└── README.mdThe step using diff-metrics would look like this:
uses: autometrics-dev/diff-metrics@v1
with:
gh-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
rust-roots: |
project-a
project-b
project-cLanguage support
You can follow the issues in the source repository (opens in a new tab) to see the advancement of language support. All languages in the table will be eventually supported.
| Language | Support |
|---|---|
| Rust (opens in a new tab) | ✅ |
| Typescript (opens in a new tab) | ✅ |
| Go (opens in a new tab) | ⚠️ |
| Python (opens in a new tab) | ✅ |
| C# (opens in a new tab) | ✅ |